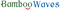The expansion of digital access makes the world better or just worsens the problem of digital divide more serious? Study the cases in Hong Kong.
Meeting the need of becoming knowledge based society and taking advantage of the innovative nature of information communications technology (ICT), Hong Kong is finding the ways to get everyone online so as to acquire worldwide knowledge and benefits from efficient digital information delivery. Therefore, the Hong Kong government, local non-profit institutions and many private companies are trying to implement wide scale infrastructures of internet networks. There is no doubt that Hong Kong become digital technology - oriented. We rely on it in a great extent. However, it is possible for some Hong Kong people, especially the poor, have obstacles getting access to ICT. As most of us have been using ICT to make our living better off, those poor people who have no or less opportunities from connecting to ICT, are marginalized group in digital century. They are also said to be under exploitation of digital divide.
In this essay, I will discuss the recent situation of digital divide in Hong Kong and discuss what factors contribute to this problem. Finally, I will give judgment to Hong Kong’s digital technology development.
Digital divide in Hong Kong
Before discussing the index of ICT usage and penetration in Hong Kong, I would like to define what digital divide is. This will make us have a better understanding of this problem.
According to the Organisation for Economic Cooperation & Development (OECD), digital divide means “the gap between individuals, households, businesses and geographic areas at different social-economic levels with regard both to their opportunities to access information and communication technologies (ICT) and to their use of the Internet for a wide variety of activities.” This board definition is merely based on a superficial understanding of the internet’s relationship to economic and social changes. Paul Gorski stresses the concept more clearly, “The term digital divide has traditionally described inequalities in access to computers and the Internet between groups of people based on one or more social or cultural identifiers.” What he mentioned shift our focus on the word “inequalities”. This extend our horizon that digital divide can be regard as a form of social inequality. Perhaps, we should say a kind of social exclusion, since their meaning are so similar. “Social exclusion is a rupturing of the social bond. It is a process of declining participation, access, and solidarity. At the societal level, it reflects inadequate social cohesion or integration. At the individual level, it refers to the incapacity to participate in normatively expected social activities and to build meaningful social relations.” Therefore, the problem of digital divide represents the marginalized group lacks various kinds of resources to adapt in the information technology based society. Mark Warschauer suggests that these resources consist of 4 forms, including physical, human, social and digital. I agree his view and but I think human, and digital aspects are the components of social aspect, so I regard them as part of as social aspects. Then, I will use physical and social resource approaches to analysis the model in Hong Kong.
Physical resource
Physical resource refers to physical availability of computer and connectivity. It means when we want to connect the internet, we should have a computer and internet service together. Without neither of it will let you fail to enter the w worldwide net. Therefore, the usage rate of personal computer and internet host rate becomes the most important indicator measuring the level of digital divide. Table one show that 74.2% of all households in Hong Kong had PC at home and 70.1% of all households had PC at home connected to the Internet. This represents a significant increase compared to the situation in 2000 when only 50% of all households in Hong Kong had PC at home and 36% of all households had PC at home connected to the Internet. We can see personal computers and Internet connections were diffused in the society. This can be explained by Hong Kong’s universal coverage for broadband Internet connections networks and highly liberalized Internet service market. Therefore, the table 4 illustrates that almost all of Hong Kong people (99%) were enjoying the highest speed internet connection service. Doubtlessly, this via broad band utilization is also amongst the highest in the world. It also means a wide variety of social and economic activities are associated with the use of the Internet. However, surprisingly, Table 2 shows that income seemed to bear a positive relationship with the rate of households having PC at home. Lower the income, lower the rate. Combining the result of the table 4 and Table 2, I found an unexpected consequence, the high internet penetration rate does not guarantee an equal access of all income groups. Although Kristopher Robison and Edward Crenshaw suggest higher the teledensity tends to have greater level of internet access, their theory is failure in case of lowest income group. Simply, it is due to the abundant choices of broadband access to community and the sufficient low service price. Thanks to the great efforts of the Hong Kong government, affordability is not their consideration anymore. The result of table 3 matches with this analysis, as only 6.8 % of poor people think that the internet service is costly. Moreover, it implies that the digital divide problem comes from insufficient digital, human and social resource of marginalized group when 64.5 % of poor people said that they did not know how to use computer and 36.5% of them see ICT with no specific application. This information clearly indicates that the Hong Kong government should move their attention into training and education.
Social resource
Mark Warschauer regards the social resource as an abstract form. In his mind, it is same as social capital. Social capital generally encompasses those social relationships that help people to get along with each other and act more effectively than they could as isolated individuals. In short, social capital can be considered as a kind of social support which is based on individuals’ social relationship in the community. Stronger your social network, more physically and mentally support you can receive from your network. Table 5 show that the main incentives of using the internet are online communication (83.3 %)and web surfing (81.3% )while the least purpose are Online data processing / analysis /database management and Self-studying online. These results illustrate the ICT facilitates the online communication. Oviously, this additional tool of communication provides chances for people forming more social circle. Surprisingly, the ICT can enhance the online communication as well as social connections, these are the valuable social capital that poor people need most. But table 4 reminds us that almost all of them found no reason to get into the digital world. It seems correct that not to close the access digital divide, is to invite increased ignorance and increased computer illiteracy. Doubtlessly, people suffering from the digital divide are more helpless to adapt the new technology. Moreover, table 5 informs the sad truth that
Hong Kong has the very high smart card utilization, but the trend cannot making peole aware and enthusiastic about the adaptability of computer knowledge. The very low penetration also fails in easing the problem of digital divide. Benefits brought about by the development of ICT are not appreciated by many sectors. The use of new digital technology is not as well as imagine.
CONCLUSION
From the above discussion, we appreciate the tremendous attempt to facilitate the physical resource of ICT. However, the insufficient social resource make this appreciable effort ran into unexpected difficulty. We should bear in mind that even though Hong Kong has highest coverage of internet networks as compared with other cities and countries in the world, digital divide is not less a problem in Hong Kong. The digital divide may be a burden for Hong Kong turning into knowledge based society and digital world. Sufficient attention should be paid to community and related computer knowledge if we wish to provide an effective access to new technology. Otherwises, the expansion of digital access would make Hong Kong less worth
Reference:
1. Hong Kong (China).Census and Statistics Dept. (2000). Thematic household survey report = 主題性住戶統計調查 ... 報告書. Hong Kong: Census and Statistics Dept.
2. Warschauer, M. (2003). Technology and social inclusion :Rethinking the digital divide. Cambridge, Mass.; London: MIT Press.
3. Wilhelm, A. G. (2004). Digital nation :Toward an inclusive information society. Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press.
4. Everard, J. (1999). Virtual states :The internet and the boundaries of the nation-state. London: Routledge.
5. Asian development bank http://www.adb.org/Documents/Books/Social_Capital/chapter01.pdf
6. social exclusion, Hilary Silver http://www.brown.edu/Departments/Sociology/faculty/hsilver/documents/hsilver-social-exclusion-encyc.pdf
7. Understanding the Digital Divide, OECD, 2007.
http://www.oecd.org/document/51/0,2340,en_2649_33757_1814131_1_1_1_1,00.html
8. Understanding the Digital Divide from a Multicultural Education Framework by Paul Gorski,2001
http://www.edchange.org/multicultural/net/digdiv.html
Survey period# Households with personal computer at home
Average Rate Households with personal computer+ at home connected to Internet Average Rate
Jan - Mar 1998 34.5 11.8
Jan - Mar 2000 49.7 36.4
Apr - Jun 2001 60.6 48.7
May - Jul 2002 62.1 52.5
May - Aug 2003 67.5 60
Jun - Aug 2004 71.1 64.9
May - Aug 2005 70.1 64.6
Jun - Aug 2006 71.7 67.1
Jul - Sep 2007 74.2 70.1
Table 1 Households with personal computer at home rate and Households with personal computer+ at home connected to Internet rate
Source: Household Survey on Information Technology Usage and Penetration, (Census and Statistics Department, Hong Kong)
Monthly household income (HK$)
%
Rate*
< 10,000 13.6 32.6
10,000 - 19,999 27.6 74.6
20,000 - 29,999 23.6 88.4
30,000 - 39,999 13.0 92.7
40,000 - 49,999 8.1 95.3
50,000 14.0 95.8
Overall 100.0 70.1
Table 2 Households with personal computer+ (PC) at home connected to Internet by
monthly household income
Source: Household Survey on Information Technology Usage and Penetration, (Census and Statistics Department, Hong Kong)
Reason for not having PC at home# %
Did not know how to use computer 64.5
No specific application 36.3
Had access to computer at other places 11.0
Cost too high 6.8
Lack of interest in using computer 3.3
Already had plan to purchase computer 2.3
Others 1.0
Table 3 Households without personal computer (PC) at home by reason for nothaving PC at home
Source: Household Survey on Information Technology Usage and Penetration, (Census and Statistics Department, Hong Kong)
Mode of connection to Internet# %
Via broad band 99.0
Via mobile telecommunications network
(e.g. mobile phone) 2.6
Via household telephone line 0.9
Table 4 Households with personal computer+ (PC) at home connected to Internet by
mode of connection to Internet
Source: Household Survey on Information Technology Usage and Penetration, (Census and Statistics Department, Hong Kong)
Major purpose of using Internet service# %
Communication with others 83.3
Browsing / surfing the web pages
(excluding Government websites) 81.3
Searching for / downloading information online (excluding
Government information) 60.3
Reading magazines / newspapers online 55.9
Online digital entertainment 37.5
Online word processing (excluding ICQ and email, etc.) 20.0
Obtain information for health 19.7
Self-studying online 5.3
Online data processing / analysis / database management 4.1
Note : # Multiple answers were allowed.
Table 5 Persons aged 10 and over who had used Internet service via mobile web device in the past twelve months by major purpose of using Internet service
Source: Household Survey on Information Technology Usage and Penetration, (Census and Statistics Department, Hong Kong)
Type of electronic business services used# Rate*
Using Octopus card for paying fare of transportation 97.3
Withdrawing / depositing / transferring moneyor checking account balance via Automatic
Teller Machine (ATM) of banks 72.4
Using Octopus card for purchasing goods andservices 66.4
Using Easy Pay System (EPS) 37.2
Purchasing goods and services via Interactive Voice Response System (IVRS) 24.8
Using telephone to settle payment by
Payment by Phone Service (PPS) 19.1
Using cyber-banking services
(e.g. transferring money) 16.8
Searching for job vacancies online 12.7
Setting payment online 11.3
Purchasing / ordering goods and services online 4.2
Donations online 0.4
# Multiple answers were allowed
Table 6 Persons aged 15 and over who had used electronic business services in the past twelve months by type of electronic business services used
Source: Household Survey on Information Technology Usage and Penetration, (Census and Statistics Department, Hong Kong)
2007年10月26日 星期五
2007年10月25日 星期四
Key visual material
An example of MMOG (Massive Multiplayer Online Game)
Tales Weaver's world
the map contains with complex and extensive continents

Tales Weaver's massive , marvelous fighting scene
many of avatars play in group to kill monsters
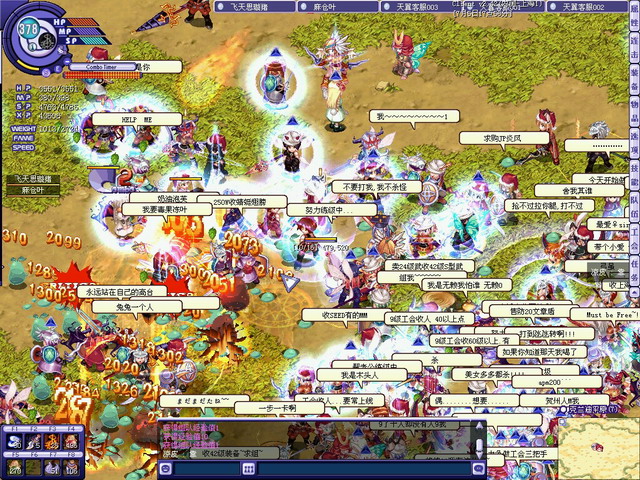
some are chatting in the games through the small message box( at the middle bottom)
Cyber space where people enjoying different kinds of online game

A very famous online game : Counter Strike (CS)
have you ever tried it??

first person perspective view

You see!! people like to play CS in group
(the right one may be killed)

The Sims, " Would you marry with me?", "Oh, yes!!I love U"
my imagination^^
Surely, you can create this scene in the game too.

Chatting is a vital part of the game

Do you want to decorate with your own dog? cat as well

.
Age of empire 2
How will you rule your kingdom if you become a king??

Will you use military force to invade the neighbor country which may be controlled by your friend?

Tales Weaver's world
the map contains with complex and extensive continents

Tales Weaver's massive , marvelous fighting scene
many of avatars play in group to kill monsters

some are chatting in the games through the small message box( at the middle bottom)

Cyber space where people enjoying different kinds of online game
A very famous online game : Counter Strike (CS)
have you ever tried it??

first person perspective view

You see!! people like to play CS in group
(the right one may be killed)

The Sims, " Would you marry with me?", "Oh, yes!!I love U"
my imagination^^
Surely, you can create this scene in the game too.

Chatting is a vital part of the game

Do you want to decorate with your own dog? cat as well

.
Age of empire 2
How will you rule your kingdom if you become a king??


Key quotes
- Synthetic worlds : the business and culture of online games / Edward Castronova, p.4
"Synthetic worlds: crafted places inside computes that are designed yo accomodate large number of peoples. - Synthetic worlds : the business and culture of online games / Edward Castronova, p.7
Lawrence Lessig (1999),the unusal thing about the cyber world is is that we can both here and there at the same time - Synthetic worlds : the business and culture of online games / Edward Castronova, p.50
Synthetic worlds may affect the dairy lives of people who have no idea what the internet is. - Mackenzie Wark Allegory on the Sims, p.3
To play the game means to play the code of a game. To win means to know the system - Play between worlds : exploring online game culture / T.L. Taylor. p.12
but I have been experimenting quite a bit , and the one thing that I 've found most interesting is , that people treat you based on how you present yourself , and, if you play attentions, you'll notice that *you* change depending on how you present yourself. - Game cultures : computer games as new media / Jon Dovey and Helen W. Kennedy, p.3
Games are not a kind of cinema, or literature, but colonizing attempts from both these fields have have already happened, and no doubt will happen again. And again, until computer game studies emerges as a clearly self sustained academic field.
Links
- Parallel Worlds, john at silversprite dot com / http://www.dlib.org/dlib/december05/kirriemuir/12kirriemuir.html
- The Sims™ - Official Site - Find your Sims community/ http://ww1.thesims2.uk.ea.com/pages.view_frontpage.asp
- Xbox online gaming main page / http://www.xbox.com/en-US/live/?WT.svl=nav
- Playstation online gaming main page / http://asia.playstation.com/eng_hk/index.php?q=playstation_network
- popcap games online gaming main page / http://www.popcap.com/online_games.php
- nintendo / http://www.nintendo.com/home
My annotated bibliography
- (Book)Game cultures : computer games as new media / Jon Dovey and Helen W. Kennedy
(useful, informative about the history of game culture) - (Book)Synthetic worlds : the business and culture of online games / Edward Castronova
(insight to me, describe some psychological aspect of online game culture) - (Book)Trigger happy : the inner life of videogames / Steven Poole
(a little bit irrelevant ) - (Book)Mackenzie Wark Allegory on the Sims
(close and highly related material ) - Play between worlds : exploring online game culture / T.L. Taylor.
(just some parts of the book are relevant) - (article)Fact Sheet:Video Game / Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, Documentary Zone
(not so relevant, but can be seen as additional information ) - (e-journal) Learning and Information Goods in Online Environments/Rutgers The State University of New Jersey - New Brunswick, 2001
(related to commercial aspect) - (e-journal) Www.Dynamicgames.Com : An Application of Dynamic Game Theory to the Analysis of E-Commerce
(related to commercial aspect) - (Book) Participating in online gaming : young people's views on avoiding committing offences & protecting personal cyber property
(local source about online culture) - (videorecording)點解兒童不宜 /Radio Television Hong Kong (RTHK)
- Parallel Worlds, john at silversprite dot com /
http://www.dlib.org/dlib/december05/kirriemuir/12kirriemuir.html
(reliable,as it provides the list of reference) - The Sims™ - Official Site - Find your Sims community/ http://ww1.thesims2.uk.ea.com/pages.view_frontpage.asp
(An important website for researching, as I have not ever played THE SIMS before) - Xbox online gaming main page / http://www.xbox.com/en-US/live/?WT.svl=nav
( useful, informing that online gaming does not restricted to computer game) - Playstation online gaming main page / http://asia.playstation.com/eng_hk/index.php?q=playstation_network
( useful, informing that online gaming does not restricted to computer game) - popcap games online gaming main page / http://www.popcap.com/online_games.php
(other kinds of free online games) - nintendo / http://www.nintendo.com/home
(similar as Xbox , and PS)
My research questions
- what are the relationship and the linkages between the cyber world and the real world
- what is the fundamental insights of online game culture
- How do people perceive online game and why they immerse in
- what are the effects of widespread growth of the online gaming industry? what are the advantages and disadvantages of this phenomenon?
訂閱:
意見 (Atom)